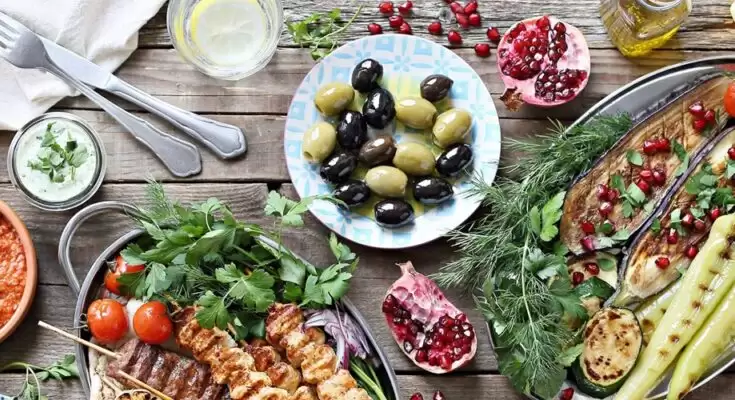
The Mediterranean Diet is a healthy eating philosophy that places a focus on local fare and customary cuisine from the countries that border the Mediterranean Sea. There are several proven health benefits, including a decreased risk of heart disease, diabetes, cancer, and stroke.
The mainstays of the diet include eating a lot of fruits and vegetables, whole grains, olive oil, and fish in moderation, limiting red meat intake, eating little dairy, eating little nuts and seeds, occasionally indulging in moderation, flavouring food with herbs and spices rather than salt, and consuming few processed foods. Exercise is also advised in addition to this diet. With the help of this guide, learn why it’s a fantastic diet option for anyone seeking for a sustainable energy meal plan.
Foods Consumed on the Mediterranean Diet
The Mediterranean Diet emphasises the consumption of high-protein foods like fish, lean meats like chicken or turkey, and legumes like beans and lentils.
Any Mediterranean Diet meal plan should include a significant amount of fruits and vegetables, which also add flavour to meals while supplying vitamins, minerals, fibre, antioxidants, and phytonutrients that support general health.
Dietary fats that are healthy, such as those found in nuts, seeds, and olive oil, are crucial. They offer vital minerals including potassium, vitamin E, and omega-3 fatty acids. Other essential elements including monounsaturated fat are also abundant in avocados.
Comparing Mediterranean Diet to Other Popular Diets
The ketogenic diet emphasises restricting carbs and substituting them with healthy fats like avocados, nuts, olive oil, and fatty fish. It is a high-fat, low-carbohydrate diet. Due to its impact on hormones like insulin, it is thought to result in better physical performance and more mental clarity.
Whole foods, fresh produce, lean proteins, olive oil, avocado, nuts and seeds, and moderate exercise are the main components of the Mediterranean diet. Indulgences and delights from time to time are acceptable in moderation.
Similar to the Ketogenic Diet, the Low-Carb Diet has less stringent limitations on the use of carbohydrates. Any diet should contain fresh fruits and vegetables since they are crucial for supplying the body with the energy it needs. White breads and pastas as well as sugary snacks are prohibited on the ketogenic diet.
Typically, the Low Fat Diet keeps daily total fat consumption under 30% of total calories, with no more than 10% coming from saturated fats. It places a focus on nutritious grains with less processing and plant-based meats like tofu and tempeh.
Creating a Mediterranean Diet Meal Plan
The Mediterranean Diet emphasises the importance of breakfast, which might include whole grain toast with olive oil and fresh tomatoes, yoghurt with nuts and seeds, porridge with fruit on top, poached eggs over greens, savoury crepes, or a smoothie made with seasonal fruits and almond milk.
Salads, roasted eggplant, grilled chicken, quinoa tabouli, tuna Nicoise salad, and falafel pita sandwiches are just a few of the nutritious lunch alternatives that are part of the Mediterranean Diet. Popular options include salads, grilled chicken, quinoa tabouli, tuna Nicoise salad, and falafel pita sandwiches.
When on a diet, grilled salmon, vegetable soup, couscous, penne pasta primavera, and vegetarian lasagne are all excellent supper choices. These consist of ricotta cheese, spinach, zucchini, cherry tomatoes, and slices of eggplant.
Exercising on the Mediterranean Diet
Exercise is crucial for general health and well-being because it lowers stress, enhances cardiovascular health, helps control weight, builds muscle strength and endurance, and enhances concentration and mental clarity. Adults should engage in physical activity for at least 30 minutes each day.
Activity options that are ideal for the Mediterranean Diet include aerobic activity, weight training, yoga, and Pilates courses. A wonderful approach to burning calories while still enjoying the outdoors is to engage in aerobic activity for at least 30 minutes per day, such as walking or running. While enhancing metabolism, strength training with weights or bodyweight activities like push-ups and squats may help contour the body and add muscular mass. An excellent approach to stretch out sore muscles after a workout is to take a yoga or pilates session, which also encourages awareness and relaxation techniques to lower stress levels.
When it comes to exercise, consistency is crucial, so be sure to stay with what you like and work it into your daily routine. Gardening, swimming laps in the pool, playing basketball, and taking frequent walks are a few things that may be done without setting up a specific time for exercise.
Conclusion
Those wishing to improve their lifestyle and health should consider the Mediterranean Diet. It has been connected to a lower risk of obesity, enhanced cardiovascular health, and a lower incidence of several illnesses like diabetes, cancer, heart disease, and Alzheimer’s. Due to its emphasis on complete meals packed with necessary vitamins and minerals, it can also assist in lowering stress levels and enhancing mental clarity.
Moderation is important while making the switch to this eating pattern. Regular exercise is also advised, as is meal planning. Anyone may begin adopting the advantages of the Mediterranean Diet into their lifestyle right now if they keep these pointers in mind.